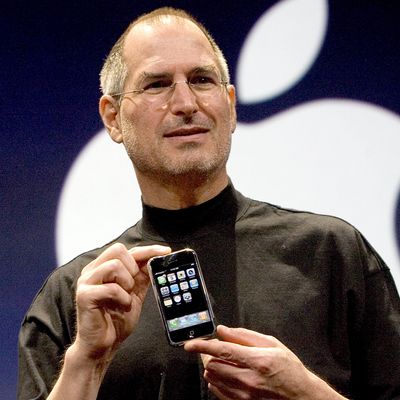
Ten years ago today, Steve Jobs took the stage at Macworld and showed off a new device. You know the spiel. “So, three things: a widescreen iPod with touch controls. A revolutionary mobile phone. And a breakthrough internet communications device. An iPod. A phone. And an internet communicator. An iPod. A phone — are you getting it? These are not three separate devices. This is one device! And we are calling it iPhone.”
Brian McCullough of the Internet History podcast pulls together a good collection of memories from the day of the event itself, showing how much of Jobs’s presentation was held together with tape and glue to ensure his brand-new device was successful, unlike Apple’s previous foray into cell phones, the little-loved and little-remembered Motorola Rokr.
After two-and-a-half years of extremely secretive work on what Apple code-named “Project Purple,” Jobs was ready to take the stage at the Moscone Center and show off the iPhone. The problem was that the iPhone itself wasn’t quite ready.
Jobs rehearsed his presentation for six solid days, but at the final hour, the team still couldn’t get the phone to behave through an entire run through. Sometimes it lost internet connection. Sometimes the calls wouldn’t go through. Sometimes the phone just shut down.
Per Andy Grignon, senior radio engineer for the iPhone: “Very rarely did I see him become completely unglued. It happened. But mostly he just looked at you and very directly said in a very loud and stern voice, ‘You are fucking up my company,’ or, ‘If we fail, it will be because of you.’”
Of course, if the iPhone failed onstage, it was because the prototype Jobs would be demoing was a bug-filled nightmare. From Fred Vogelstein’s 2013 write-up in The New York Times Magazine:
The iPhone could play a section of a song or a video, but it couldn’t play an entire clip reliably without crashing. It worked fine if you sent an e-mail and then surfed the Web. If you did those things in reverse, however, it might not. Hours of trial and error had helped the iPhone team develop what engineers called “the golden path,” a specific set of tasks, performed in a specific way and order, that made the phone look as if it worked.
Jobs also wanted to make sure that connectivity wasn’t an issue for the iPhone. But to do that required some shading around the edges. From the same Times Magazine report:
They had AT&T, the iPhone’s wireless carrier, bring in a portable cell tower, so they knew reception would be strong. Then, with Jobs’s approval, they preprogrammed the phone’s display to always show five bars of signal strength regardless of its true strength.
Jobs had more than just the reputation of the iPhone to contend with. CES was happening at the same time, and it was Jobs’s hope that the iPhone would steal headlines away from whatever was being debuted in Vegas that day. But there was still a nagging problem: In virtually every rehearsal Jobs had done with the phone, it would run out of memory at some point, causing the phone to crash and restart. The only fix was to have multiple backups on hand.
Jobs had a number of demo units onstage with him to manage this problem. If memory ran low on one, he would switch to another while the first was restarted. But given how many demos Jobs planned, Grignon worried that there were far too many potential points of failure. If disaster didn’t strike during one of the dozen demos, it was sure to happen during the grand finale, when Jobs planned to show all the iPhone’s top features operating at the same time on the same phone. He’d play some music, take a call, put it on hold and take another call, find and e-mail a photo to the second caller, look up something on the Internet for the first caller and then return to his music.
McCullough goes on to explain what happened after — how Jobs had to be convinced to actually create an App Store (he wanted developers to simply do everything in Safari), and the struggle to get the next version of the iPhone, the iPhone 3G, off the slow-as-hell Edge data networks.
Jobs unveiling the iPhone is often pointed to as the pinnacle in tech presentations — one of the few times where the hype and grandeur actually matched the device on display. But it wasn’t just a master class in marketing and showmanship; it was a technological roll of the dice that ended up changing the world.