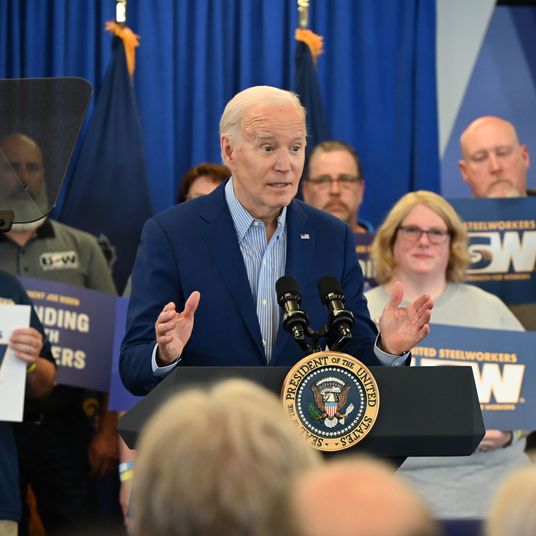
There are hints in the air that the long-predicted ideological schism within the Republican Party between populists and traditional conservatives is breaking open. Donald Trump’s unusually populist inaugural address, almost devoid of traditional conservative themes, seemed to break new ideological ground. Unlike most Republicans who try to ape the rhetorical tropes associated with Ronald Reagan, Trump instead tried to recall the stylings of Andrew Jackson. “It was an unvarnished declaration of the basic principles of his populist and kind of nationalist movement,” chief strategist Steve Bannon told the Washington Post. “I don’t think we’ve had a speech like that since Andrew Jackson came to the White House,” Bannon said. “But you could see it was very Jacksonian.” Meanwhile, Trump has hired Julia Hahn, a 25-year-old Breitbart staffer who has savaged Paul Ryan for his past support for immigration reform, alarming allies of the House Speaker.
It is certainly true that ideological tensions exist between Trump and the party he has conquered. Trump is surely not a traditional conservative, for the simple reason that conservatism is a set of relatively coherent policy beliefs, and Trump does not have very many coherent policy beliefs. But the beliefs he does have, at least as far as we can tell from his administration and his agenda, overlap heavily with traditional conservatism. That is because the conservative tradition and the populist Jacksonian tradition turn out to be mostly the same thing.
The points of difference between Trump and Ryan are smaller than they might appear. Ryan has supported comprehensive immigration reform in the past, and continues to support free trade, while Trump opposes both. Neither disagreement is especially difficult to finesse. The only major new trade agreement on the docket, the Trans-Pacific Partnership, was already moribund before the election. Comprehensive immigration reform died three years ago, and Trump has already backed off his promises to quickly deport Dreamers and is focusing instead on border-security measures that enjoy long-standing Republican support.
Meanwhile, the Congressional party is working hand-in-glove with its presidential wing. Every Trump cabinet nominee, even those who are brutally unqualified (like Ben Carson) or laden with serious ethical problems (like Tom Price), seems likely to sail through a Senate that can only afford to lose two Republican votes. And Congress has allowed Trump to conceal his tax returns and maintain his business empire, two violations of norms that would permit massive self-enrichment by the president and his family. Republicans have instead directed the oversight machinery of Congress against Trump’s critics and former opponents.
Trump and his party are cooperating on a wide range of traditional Republican policies: regressive tax cuts, weakening of labor laws, environmental protections, and regulations on the finance industry, and an assault on the Affordable Care Act. Both Trump and the Congressional GOP have attacked Obamacare for providing too little coverage, and have refrained from writing detailed alternatives because their ideas would provide even less coverage. To the extent that Trump is giving his Congressional wing trouble on health care, it is because he spouts off without understanding the issue.
The differences between Trump and his Congressional allies are no wider than those that divided Barack Obama and his party in 2009, or George W. Bush and his party eight years before that, or Bill Clinton and his eight years prior. Tim Phillips, president of the Koch-backed Americans for Prosperity, the epitome of the libertarian, pro-business, Paul Ryan–esque Republican money wing, has praised Trump’s policies. “There just isn’t much daylight between us,” he told Politico recently.
What, then, explains the widespread belief that Trump has veered so far from traditional Republican doctrine? One reason is emphasis. Trump simply ignores the traditionally Republican elements of his governing program in his public remarks. Trump devoted most of his inaugural speech to the few elements of his platform that diverge from the Paul Ryan agenda, skipping over the many elements that conform to it. And he compounded the impression, as he has during the campaign, by portraying himself as an enemy of the elite and the political class.
But there is another thing that is necessary to grasp about the political tradition Trump represents. Jacksonian populism is conservatism, at least in the modern American form.
While nearly two centuries have passed since Andrew Jackson’s time, he pioneered almost every recognizable feature of contemporary Republican politics. Jackson built a following by denouncing elites. But he did not mean economic elites, exactly. He meant Easterners, urbanites, and experts, including the ones who argued a national bank was necessary to avoid a financial crisis. (They were right and Jackson was wrong. Jackson’s destruction of the bank caused a serious recession.) Jackson did not oppose bankers, per se — he drew support of regional banks that felt threatened by the national bank. Jackson had no program of taxing or regulating the rich. His economic populism was directed entirely against the state. “The rich and powerful too often bend the acts of government to their selfish purposes,” he wrote.
Many people understand that Jackson’s reputation has come under harsh scrutiny and revision in recent decades, in part because he “owned slaves.” Of course, many (though not all) political elites owned slaves before the Civil War. It is not just that Jackson owned slaves but that he followed policies to protect and defend slavery, as opposed to the conflicted positions of other slave-owning politicians who wished to see the practice end eventually. Jackson’s conquest of Native American lands — the cruelty of which provoked strong domestic opposition — was carried out for the purpose of expanding slave territory, in order to prevent the slave states from being outnumbered and eventually outvoted (the fear among slave states that led, via the Missouri Compromise, to the Civil War). Jackson banned the mailing of abolitionist literature into the South. As the cast of America’s racial hierarchy has changed over its history, the meaning of the right-wing and left-wing positions on the racial question has evolved. In Jackson’s time, his position of expanding land available for slavery and blocking avenues for organizing opposition to it clearly represented the right-wing position.
Jackson’s resemblance to Trump runs even deeper than Trump or Steve Bannon may realize. Jackson, like Trump, throbbed with resentment at his enemies, a feeling that was channeled into extraordinary personal entitlement. (As Steve Inskeep discovers in Jacksonland, Jackson used his office to enrich himself by speculating in lands whose value he knew would increase as a result of his conquests.) Jackson opposed South Carolinian secession for the same reason he dismissed a hostile Supreme Court ruling — not out of any larger principle, but out of a domineering instinct that made him lash out instinctively at any threat to his authority. That style endeared him to the part of the country that forms the base of the GOP today. Jackson fused the white working class in the South and Appalachia with the interests of the planter elite, expressing their shared interests not through activist government but through militaristic plunder.
An aura of progressivism has clung to Jackson for decades, largely due to an accident of history. During the 19th century, the Democratic Party was the conservative, Southern, rabidly white-supremacist, strict constructionist party, while the Whigs, and then the Republicans, favored more activist government and more egalitarian social structure. During the 20th century, those roles reversed. But the Democratic Party retained its Southern and Appalachian base for decades during the transition, and it convinced itself of a narrative (using wildly selective history) that wove Jackson’s reactionary presidency into the 20th-century version.
Meanwhile, as the Republican Party has grown more uniformly conservative, it has naturally grown more Jacksonian in its style. The cultural populism, anti-intellectualism, paranoia, and crude nationalism of such figures as Joe McCarthy, George Wallace, and Sarah Palin presaged the buffoonish ravings of the current president. Far from being at odds with the agenda of a party allied with entrenched wealth, that populist style is the best way to lend that agenda mass appeal. We should stop seeing Trumpism as a challenge to the GOP and instead understand it as the party’s natural historical evolution.